Trump’s Interest in Greenland: A Strategic Move Beyond Minerals
President Donald Trump’s interest in Greenland extends beyond the allure of its mineral wealth and territorial expansion. The motivations are deeply rooted in geo-economic factors, particularly concerning military positioning and shipping routes. Greenland’s strategic location in the Arctic has drawn attention from both the Trump and Biden administrations, highlighting the increasing significance of the region as climate change alters navigability.
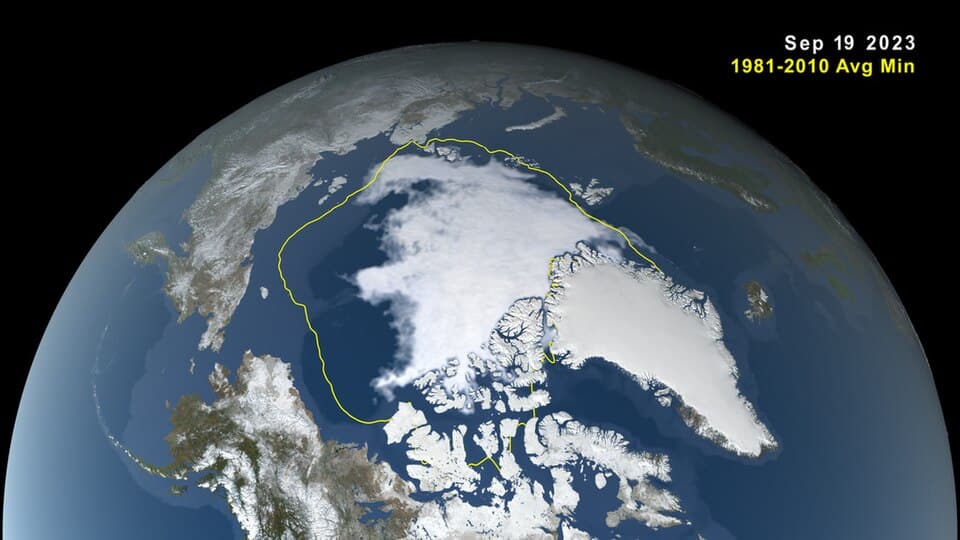
The Arctic is a focal point for global powers, with Russia holding a dominant position. With approximately 15,000 miles of Arctic coastline compared to the United States’ 1,060 miles, Russia’s presence is formidable. Control over Greenland would significantly enhance the U.S. footprint in the Arctic, a goal that aligns with the 2024 U.S. Arctic Strategy, which emphasizes the importance of the region as melting sea ice opens new chokepoints for navigation and military operations.
The Biden administration’s Arctic Strategy has raised alarms in Moscow, suggesting that the U.S. is preparing for potential confrontations to safeguard its interests. NATO’s Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg previously indicated the need for an increased NATO presence in the Arctic, a sentiment echoed by the accession of Finland and Sweden to the alliance. However, the omission of Denmark from the Arctic Strategy’s executive summary raised eyebrows, indicating potential diplomatic oversights that could affect U.S.-Denmark relations.
Economic and Shipping Implications of Greenland Control
The economic potential of Greenland is substantial, with vast natural resources critical for technology and energy sectors. Approximately 80% of Russia’s gas and 20% of its oil are sourced from Arctic territories, underscoring the region’s importance. Greenland is believed to contain significant reserves of minerals essential for electronics and military technologies, making it a target for U.S. interests.
Moreover, the Arctic’s shipping routes are becoming increasingly vital. Russia has developed the Northern Sea Route, which drastically reduces shipping times between Europe and East Asia. This route offers a significant advantage over traditional paths, such as the Suez Canal, by cutting travel distances and time. Conversely, the Northwest Passage, which runs through Canada and Alaska, is mired in legal disputes regarding its status as internal waters. Control of Greenland would shift the balance of power, allowing the U.S. to anchor both the Bering Sea and Atlantic choke points, enhancing military navigation across the Arctic.
Current tensions between the U.S. and Canada, particularly under Prime Minister Mark Carney, may also play a role in Trump’s Greenland strategy. By asserting claims over Greenland, the U.S. could pressure Canada into negotiations regarding the Northwest Passage, potentially reshaping the dynamics of Arctic governance.
As the geopolitical landscape continues to evolve, the U.S. administration’s focus on Greenland is likely to persist. With Greenlanders holding the right to self-determination under a 2009 Act, the complexities of sovereignty and international relations will remain at the forefront of discussions surrounding this strategically significant territory.
